Cardiac Anatomy and Coronary Circulation
Gross Anatomy of the Heart
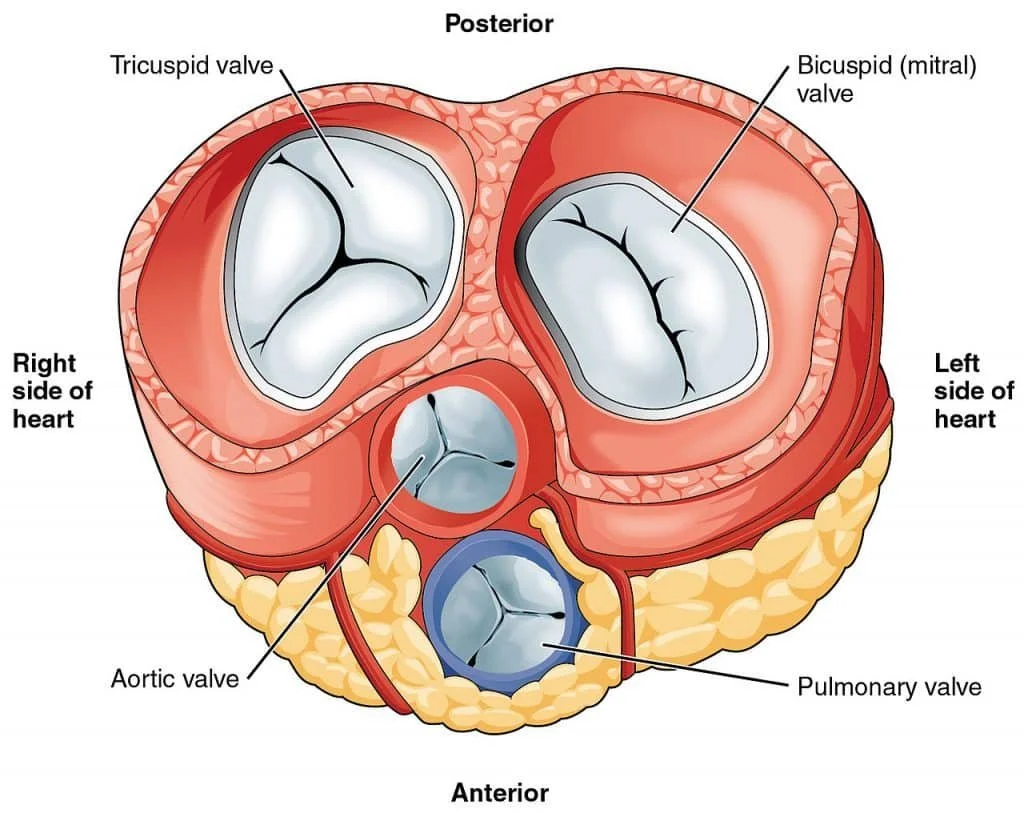
Chambers & Valves
Right Atrium: Receives deoxygenated blood from the superior and inferior vena cava.
Right Ventricle: Pumps blood to the lungs via the pulmonary artery.
Left Atrium: Receives oxygenated blood from the pulmonary veins.
Left Ventricle: Pumps oxygenated blood to the body via the aorta.
Valves:
Atrioventricular Valves: Tricuspid (right), Mitral (left).
Semilunar Valves: Pulmonary, Aortic.
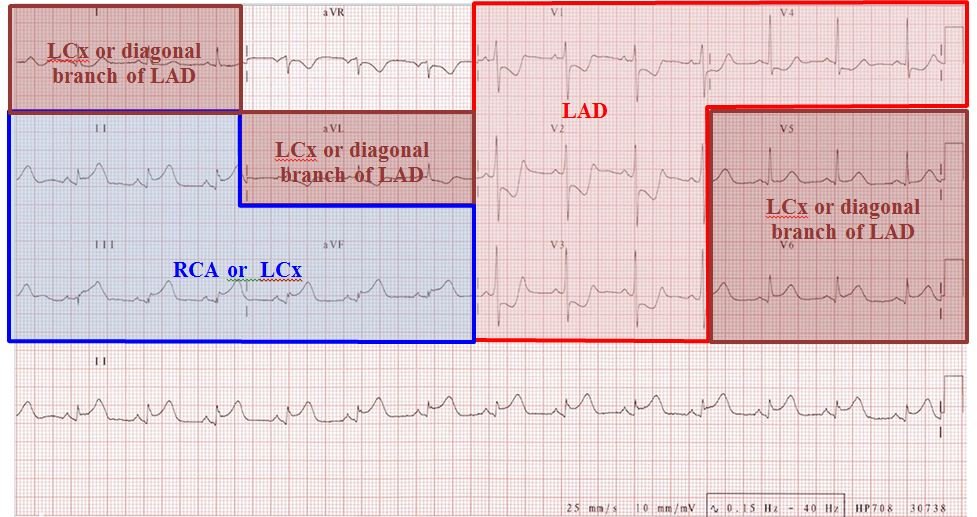
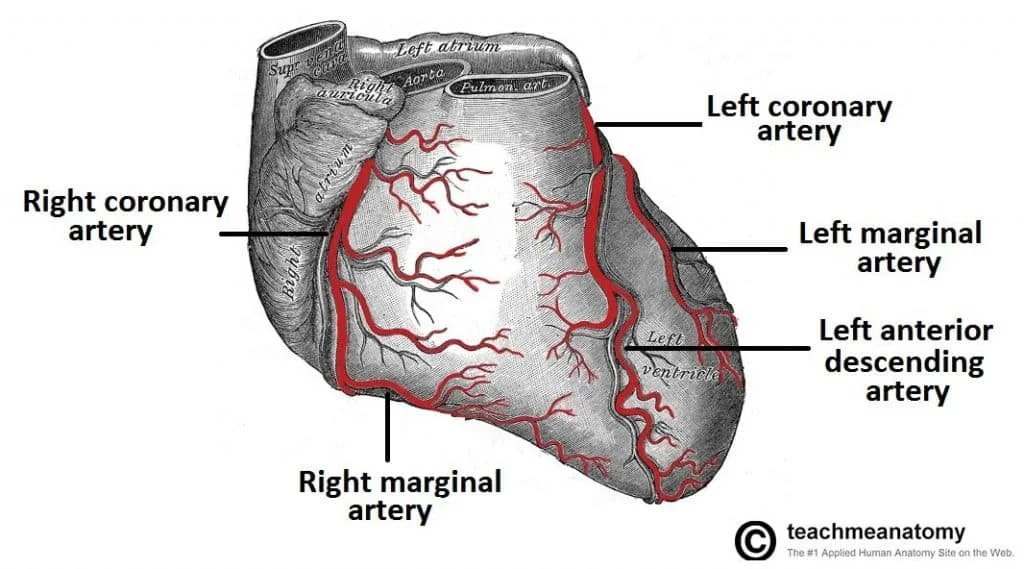
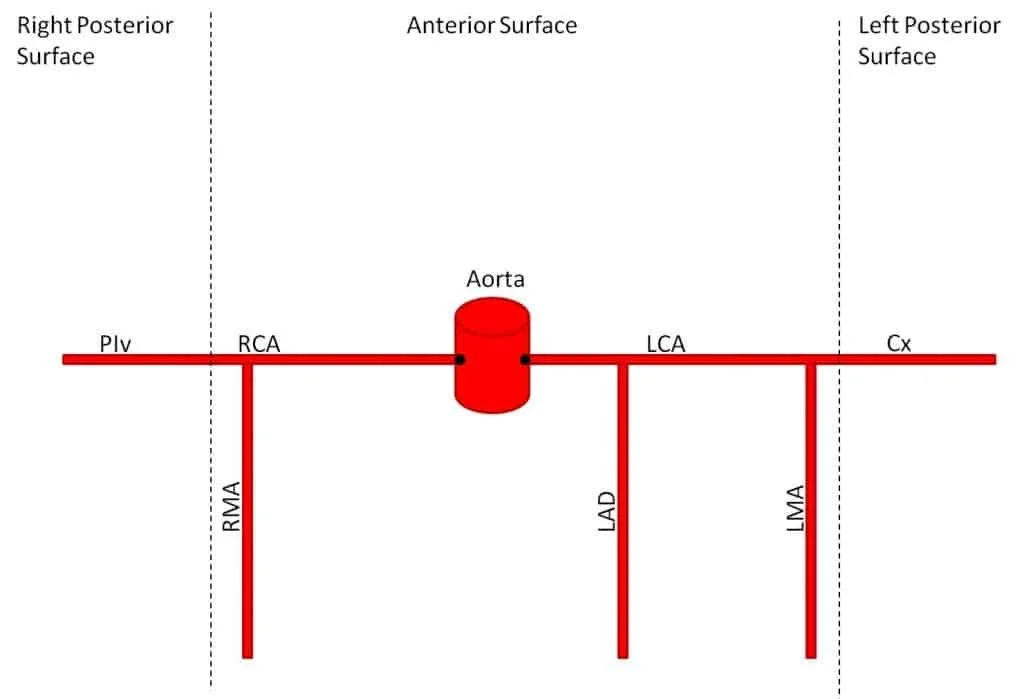
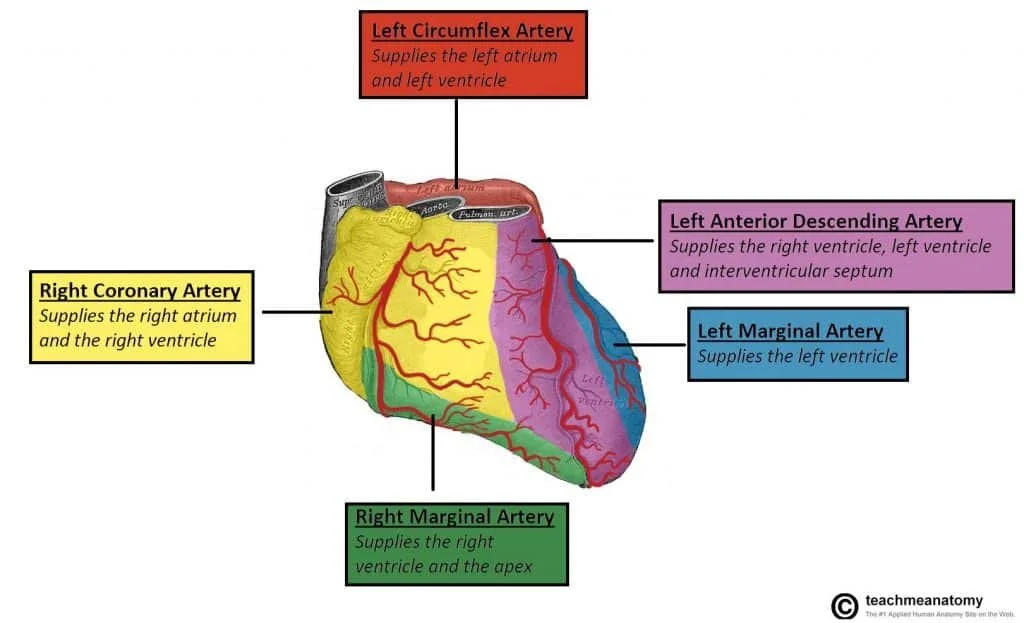
The heart has a dual blood supply system from the left and right coronary arteries, originating from the aortic root.
A. Left Coronary Artery (LCA) & Its Branches
Left Main Coronary Artery (LMCA): Short segment before bifurcation.
Left Anterior Descending Artery (LAD):
Supplies anterior LV, anterior 2/3 of interventricular septum.
Gives off diagonal and septal perforator branches.
Left Circumflex Artery (LCx):
Supplies lateral LV wall.
Gives off obtuse marginal (OM) branches.
In some cases, it contributes to the posterior descending artery (PDA) in a left-dominant circulation.
B. Right Coronary Artery (RCA) & Its Branches
RCA: Originates from the right coronary sinus of the aorta.
Major branches:
Right Marginal Artery: Supplies RV lateral wall.
Posterior Descending Artery (PDA): Supplies posterior 1/3 of the septum in right-dominant circulation (85% of cases).
SA Nodal & AV Nodal Arteries: Important in conduction system blood supply.
C. Coronary Artery Dominance
Right-Dominant Circulation (85%): PDA arises from RCA.
Left-Dominant Circulation (10-15%): PDA arises from LCx.
Co-Dominant Circulation (~5%): PDA arises from both RCA and LCx.